Irregular Periods After Steroid Injections – Cause, Treatment, and Prevention

Steroid injections are commonly used for various medical conditions such as joint pain, inflammation, and allergies. While they can effectively treat these conditions, they may also have unwanted side effects, such as irregular periods.
So, what causes irregular periods after steroid injections, and how can this be treated?
Steroid injections can affect hormone balance, causing irregular periods. Anabolic steroids may cause abnormal menstrual cycles, while corticosteroids can lead to intermenstrual bleeding or delayed periods. Treatment options include hormonal birth control, progestin therapy, evaluating steroid use, and addressing the underlying condition.
In this article, we will examine why steroid injections can cause irregular periods and what steps you can take to manage this side effect. So, if you have recently had a steroid injection and are experiencing irregular periods, keep reading!
Irregular Periods After Steroid Injections
Steroid injections can disrupt the typical pattern of your periods, causing them to become irregular. This happens because steroids affect the balance of hormones in your body.
Now let’s understand the menstrual cycle and what are irregular periods to explore how steroid injections can lead to changes in your menstrual cycles.
What Are Irregular Periods?
Irregular periods refer to variations in menstrual cycle duration, timing, and flow. While the average menstrual cycle lasts around 28 days, it is considered normal for cycles to range between 21 and 35 days. Menstrual periods usually last four to seven days, which can also vary.
In the context of irregular periods, some common occurrences include:
- Frequent or Infrequent Menstruation: Menstrual cycles that occur more frequently than every 21 days or less frequently than every 35 days.
- Absent or Missed Periods: Skipping of three or more consecutive periods.
- Heavy or Light Bleeding: Experiencing significantly heavier or lighter menstrual flow compared to what is typical for an individual.
A complex interplay of hormones and processes within the female reproductive system regulates the menstrual cycle.
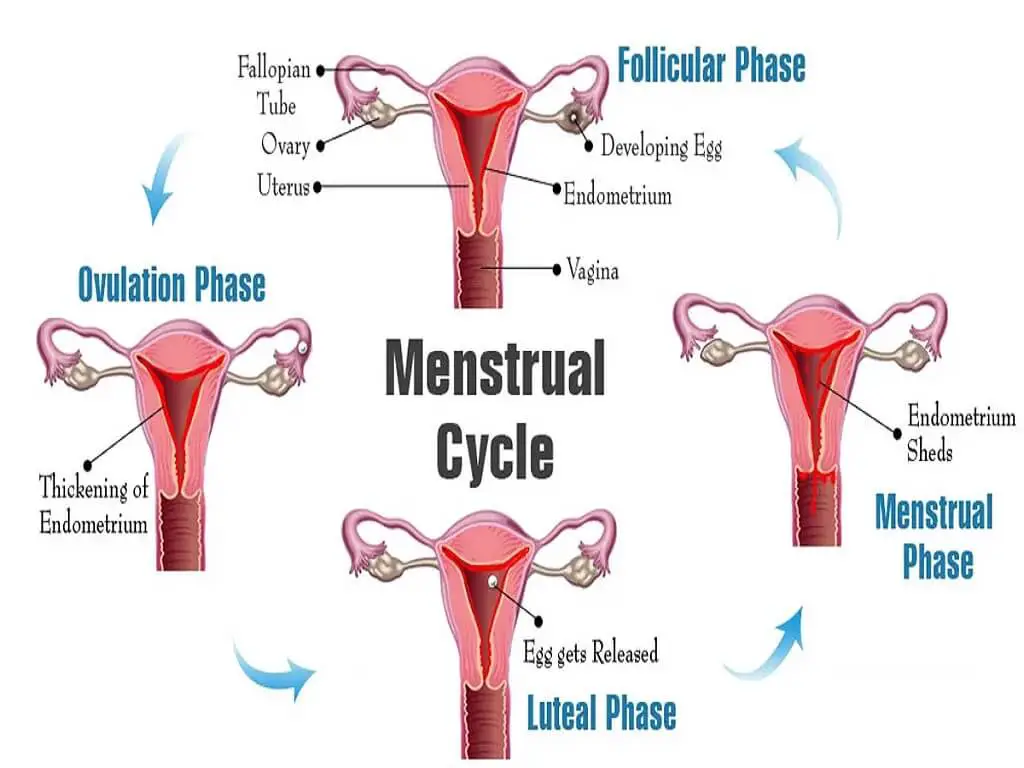
Understanding The Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of hormonal changes and events that prepare the female body for a potential pregnancy. It involves the coordination of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, ovaries, and uterus. The cycle can be divided into four phases:
- Menstrual Phase: The cycle begins with menstruation, where the uterine lining sheds if pregnancy hasn’t occurred. This phase typically lasts 3 to 7 days.
- Follicular Phase: Following menstruation, the pituitary gland releases follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulates the growth of follicles in the ovaries. Each follicle contains an egg. As the follicles develop, they release estrogen, which thickens the uterine lining.
- Ovulation: A luteinizing hormone (LH) surge triggers a mature egg’s release from the ovary. This usually occurs around day 14 in a 28-day cycle. The egg travels through the fallopian tube, awaiting fertilization.
- Luteal Phase: After ovulation, the ruptured follicle transforms into the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. Progesterone helps prepare the uterus for the implantation of a fertilized egg. If fertilization doesn’t occur, the corpus luteum disintegrates, hormone levels drop, and the next menstrual cycle begins.
Source: elara.care
Everyone’s menstrual cycle is different, and occasional cycle length or flow changes are regular. However, if you notice consistent irregularities or significant changes, it’s essential to seek medical advice.
Consulting with a healthcare provider will help identify any underlying causes. If needed, they will provide a diagnosis and offer appropriate treatment options to regulate your periods and ensure your reproductive health.
Read More: Can Avocado Cause Diarrhea?
How do Steroid Injections Cause Irregular Periods?
Steroids can disrupt the normal hormonal regulation of the menstrual cycle, leading to irregular periods. The mechanisms differ based on the type of steroid used.
-
Anabolic Steroids
Anabolic steroids are synthetic substances that mimic testosterone, and their use can impact the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, which regulates hormonal balance and menstrual cycles. Here’s how anabolic steroids contribute to your irregular periods:
Suppression of Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis: Anabolic steroids interfere with the normal functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, leading to reduced production and release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). This disruption results in lower levels of estrogen and progesterone, causing irregularities in follicle development, ovulation, and, ultimately, irregular periods.
Inhibition of Follicle Formation and Ovulation: High levels of androgens, such as testosterone, due to anabolic steroid use can inhibit the normal processes of follicle formation and ovulation. This inhibition can delay egg development and release, resulting in irregular or absent periods.
Source: elara.care
-
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids, like prednisone, are often prescribed for managing inflammatory conditions. Prolonged use of corticosteroids can affect the body’s hormonal balance, leading to irregular periods. Here’s how corticosteroids contribute to menstrual irregularities:
Suppression of the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis: Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, suppress the HPA axis, which controls the production of hormones involved in menstrual cycle regulation. This suppression disrupts the normal hormonal balance, resulting in irregular periods and abnormal bleeding.
Treatment
If you are experiencing irregular periods due to steroid injections, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider for appropriate management. Here are some potential treatment options:
-
Hormonal Birth Control
Your healthcare provider may prescribe hormonal birth control methods, such as combination or progestin-only pills, to help regulate your menstrual cycle. These medications can help restore hormonal balance and promote regular periods.
-
Progestin Therapy
Progestin therapy may be recommended to induce regular periods. This can be administered through oral medication, injections, or intrauterine devices (IUDs).
-
Evaluation of Steroid Use
Your healthcare provider may assess the necessity of continued steroid injections and find alternative treatment options that may have fewer effects on your menstrual cycle. They will consider the benefits and risks of steroid use for your specific condition.
-
Treatment of Underlying Condition
Suppose steroid injections were prescribed to manage an underlying medical condition. In that case, your healthcare provider might explore other treatment modalities or combination therapies to effectively address the situation while minimizing the impact on your menstrual cycle.
Prevention And Self-Care
It may not be possible to prevent the effects of steroid injections on menstrual regularity entirely. The following self-care measures may help support hormonal balance and overall well-being:
- Inform your healthcare provider about any concerns or changes you notice in your menstrual cycle during steroid treatment. They can provide guidance and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Your healthcare provider may recommend supplements or dietary modifications that support hormone balance. This could include consuming a nutrient-rich diet and ensuring adequate essential vitamins and minerals intake.
- Use stress reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or relaxation exercises because stress can affect hormonal balance and menstrual regularity.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle by exercising regularly, getting sufficient sleep, and following a balanced diet. Avoid extreme weight loss or gain, as these can impact hormonal levels and menstrual cycles.
- Attend regular check-ups with your gynaecologist or primary care provider to monitor your menstrual cycle and address any concerns promptly.
Consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options, considering your condition, steroid type, and individual factors for the best treatment plan.
Read More: Does Popcorn Make You Constipated?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Can Steroid Injections Cause Menstrual Bleeding?
Yes, steroid injections, such as intra-articular and epidural corticosteroid injections, have been reported to cause abnormal vaginal bleeding potentially. It can include menstrual bleeding as a side effect in some female patients. Medical professionals must inform female patients about this potential risk before undergoing such procedures.
-
Can Steroids Cause Abnormal Uterine Bleeding?
Yes, the use of steroids can potentially cause abnormal uterine bleeding in some women, leading to changes in menstrual frequency, duration, volume, and bleeding between periods.
-
Can Steroids Cause Bleeding After Menopause?
Steroids can cause a transient episode of bleeding in postmenopausal women, possibly attributed to a temporary decrease in androstenedione levels.
Conclusion
In conclusion, irregular periods after steroid Injections can occur due to the disruption of hormonal balance caused by the injections. Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial for proper management and treatment.
Hormonal birth control, progestin therapy, and evaluating steroid use may be considered for the treatment. Self-care measures and regular check-ups are essential for overall well-being and monitoring menstrual health.